
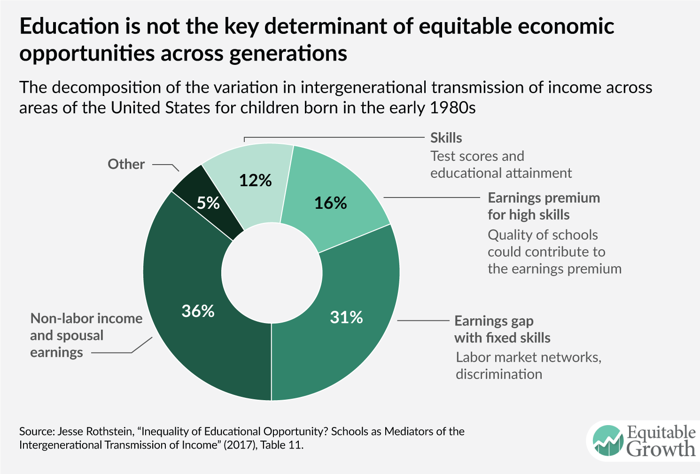
A growing body of research debunks the idea that school quality is the main determinant of economic mobility.
A body of research has since emerged to challenge this national story, casting the United States not as a meritocracy but as a country where castes are reinforced by factors like the race of one’s childhood neighbors and how unequally income is distributed throughout society. One such study was published in 2014, by a team of economists led by Stanford’s Raj Chetty. After analyzing federal income tax records for millions of Americans, and studying, for the first time, the direct relationship between a child’s earnings and that of their parents, they determined that the chances of a child growing up at the bottom of the national income distribution to ever one day reach the top actually varies greatly by geography. For example, they found that a poor child raised in San Jose, or Salt Lake City, has a much greater chance of reaching the top than a poor child raised in Baltimore, or Charlotte. They couldn’t say exactly why, but they concluded that five correlated factors—segregation, family structure, income inequality, local school quality, and social capital—were likely to make a difference. Their conclusion: America is land of opportunity for some. For others, much less so.
Indeed, this bipartisan education-and-poverty consensus has guided research and political efforts for decades. Broadly speaking, the idea is that if more kids graduate from high school, and achieve higher scores on standardized tests, then more young people are likely to go to college, and, in turn, land jobs that can secure them spots in the middle class.
Rothstein’s new work complicates this narrative. Using data from several national surveys, Rothstein sought to scrutinize Chetty’s team’s work—looking to further test their hypothesis that the quality of a child’s education has a significant impact on her ability to advance out of the social class into which she was born.
His work, like Chetty’s, is not causal—meaning Rothstein is not able to identify exactly what explains the underlying variation in his economic model. Nevertheless, his work helps to provide researchers and policymakers with a new set of background facts to investigate, and signals that perhaps they should be reconsidering some of their existing ideas. (Both Raj Chetty and his co-author Nathaniel Hendren declined to comment for this story.)
Jose Vilson, a New York City math teacher, says educators have known for years that out-of-school factors like access to food and healthcare are usually bigger determinants for societal success than in-school factors. He adds that while he tries his best to adhere to his various professional duties and expectations, he also recognizes that “maybe not everyone agrees on what it means to be successful” in life.
No comments:
Post a Comment